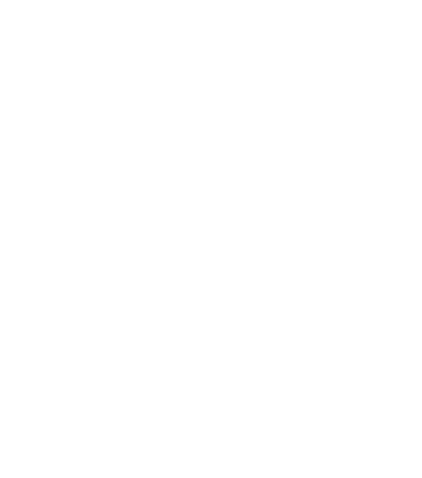
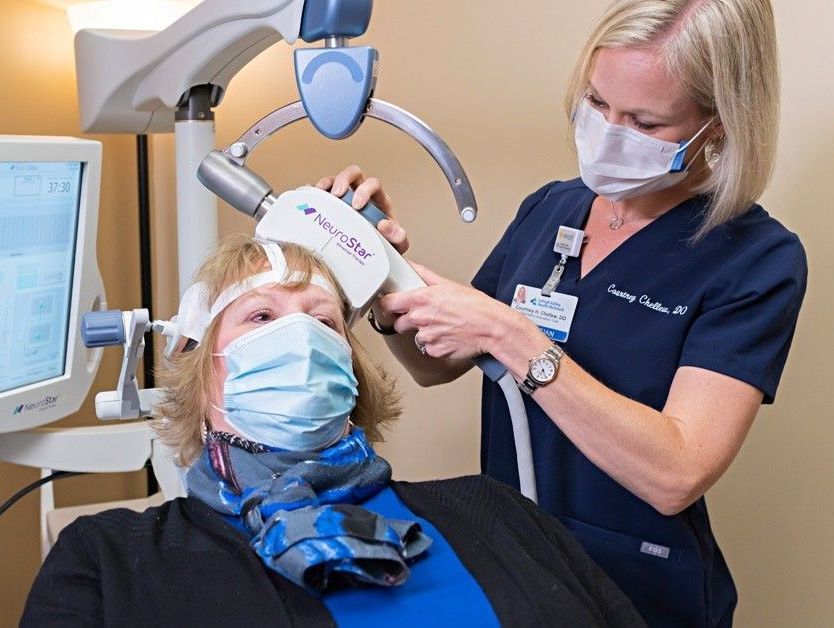
Personalized recommendations based on your needs
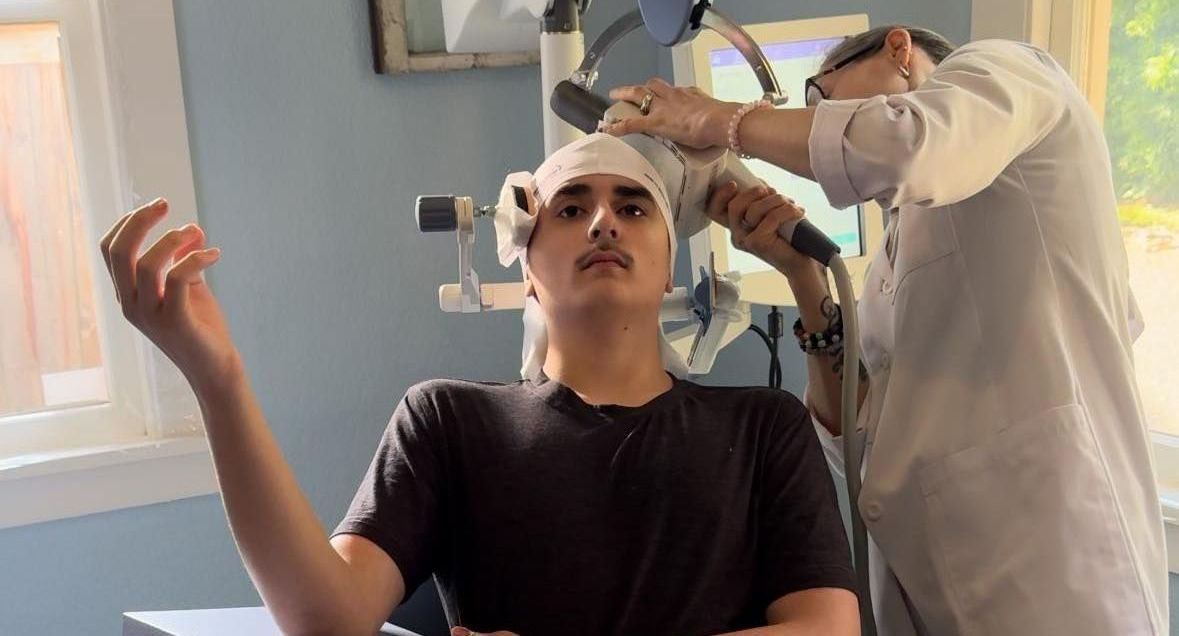
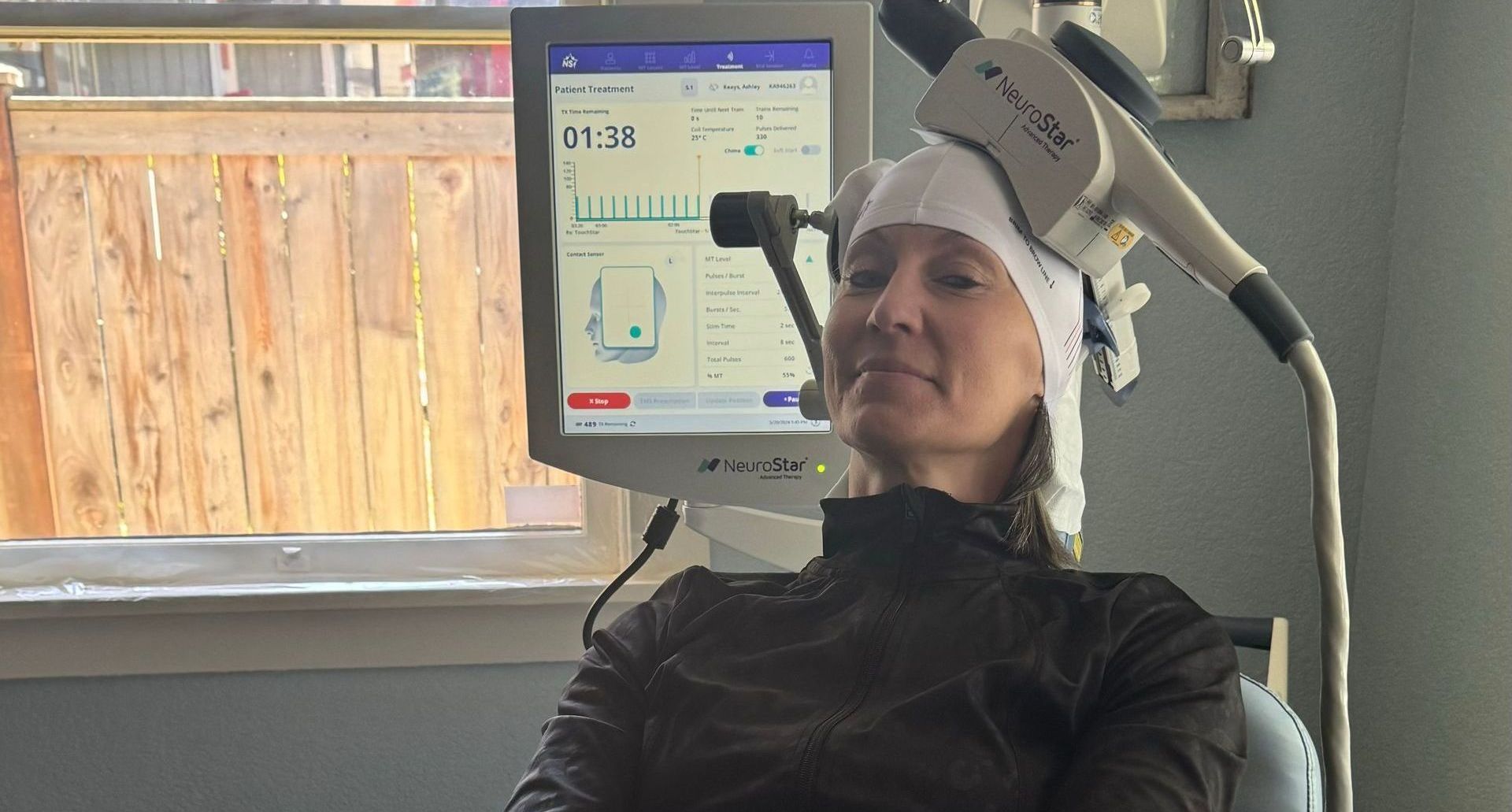
TMS THERAPY
Conditions Treated
TMS Can Be Helpful for Autism
Current Limitations & Considerations
- Still Experimental: TMS is not yet an FDA-approved treatment for autism. Research is ongoing to determine its effectiveness and long-term impact.
- Individual Variability: Results can vary significantly between individuals, and it may not work for everyone.
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental condition that can affect multiple aspects of daily life and has an extensive symptom profile unique to each individual. TMS can address associated symptoms in the following ways:
Improving Social Skills and Communication
For some people with ASD, interpersonal skills can require greater effort to develop. Nuances in body language, facial expressions, verbal tone, and other factors can be more difficult to decipher, which can hinder social connections and effective communication.
How TMS helps:
TMS has been studied for its effects on the prefrontal cortex, an area linked to social cognition.
Some studies suggest that TMS may enhance social interactions and eye contact in individuals with ASD.
Reducing Repetitive Behaviors
Self-stimulation or “stimming” is a common feature of ASD, where people engage in repetitive behaviors as a method to regulate their body or self-soothe.
How TMS helps:
Research indicates that stimulating specific brain regions (such as the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex) can help decrease repetitive and restrictive behaviors, which are common in ASD.
Enhancing Emotional Regulation
Many individuals with autism struggle with emotional regulation and anxiety.
How TMS helps:
TMS may help modulate brain activity in areas associated with mood and emotional processing, potentially reducing anxiety and emotional outbursts.
Improving Cognitive Function
Some individuals present with cognitive impairments that may potentially affect their education or occupational prospects or increase their dependency on others around them.
How TMS helps:
Some studies suggest that TMS may improve executive functioning, attention, and working memory in individuals with ASD.
Addressing Sensory Processing Issues
ASD often involves sensory sensitivities in multiple modalities (eg, auditory, visual, tactile, olfactory, and gustatory), which can create barriers in everyday life. Overstimulation can also occur where individuals may experience emotional distress or become overwhelmed with an excess of sensory input.
How TMS helps:
TMS has been explored for its role in regulating sensory processing in the brain.
TMS Can Be Helpful for Dementia
Current Limitations & Considerations
- Still Experimental: TMS is not yet FDA-approved for dementia treatment.
- Temporary Benefits: Cognitive improvements may not last long without continuous treatment.
- Varied Results: Some patients show improvements, while others experience minimal effects.
Dementia is a term for a collection of symptoms caused by various diseases characterized by neurodegeneration, coinciding with aging.
Cognitive Improvement
Dementia is often recognized by a decline in memory, problem-solving, language, and other abilities.
How TMS helps:
TMS stimulates the prefrontal cortex and other brain regions involved in memory, attention, and executive function.
Some studies suggest that TMS may help improve working memory and slow cognitive decline.
Enhancing Neuroplasticity
The breakdown of neural connections is a common factor contributing to dementia.
How TMS helps:
TMS promotes neuroplasticity (the brain's ability to reorganize and form new neural connections), which may help compensate for compromised neurons and neural pathways in dementia patients.
Boosting Brain Connectivity
Complex cognitive processes operate via communication between different networks in the brain which is compromised in presentations of dementia.
How TMS helps:
TMS may enhance communication between different brain regions that deteriorate in dementia, improving overall brain function.
Reducing Depressive Symptoms
Depression is often observed in people with dementia, and either can exacerbate the other.
How TMS helps:
TMS, particularly when applied to the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, has been shown to reduce depressive symptoms and increase motivation.
Slowing Disease Progression
Dementia can have an immense impact on daily living, independence, physical activity, thinking, and more. By slowing down the progression of symptoms, individuals can live with a greater quality of life.
How TMS helps:
Some research suggests that early and repeated TMS treatment may help slow the progression of dementia by keeping neural pathways active.
TMS Can Aid Stroke Recovery
Current Limitations & Considerations
- Not a Standard Stroke Treatment Yet: It is Still being researched, but some clinics offer it as part of rehabilitation.
- Individual Response Varies: Some patients show significant improvement, while others may see minimal effects.
- Best Used Alongside Rehabilitation: TMS works best when combined with physical therapy, speech therapy, and cognitive training.
When the brain is severely deprived of oxygen, a stroke can occur. This can lead to varying degrees of damaged neural pathways that affect cognitive, behavioral, and emotional processing.
Enhancing Motor Recovery
A stroke often damages one hemisphere of the brain, leading to weakness or paralysis on one side of the body.
How TMS helps:
Stimulating the affected motor cortex can promote neuroplasticity (the brain's ability to reorganize and form new connections).
Inhibiting the overactive, non-stroke hemisphere can reduce imbalances and improve movement in the affected side.
Improving Speech and Language (Aphasia Treatment)
Many stroke survivors struggle with aphasia (difficulty speaking or understanding language).
How TMS helps:
Targeting the left inferior frontal gyrus (Broca’s area) may improve speech production and comprehension.
Boosting Cognitive Function
Stroke can impact memory, attention, and problem-solving skills.
How TMS helps:
Stimulating the prefrontal cortex may improve cognitive processing and mental clarity.
Reducing Post-Stroke Depression
Stroke survivors often experience depression, which can slow recovery.
How TMS helps:
TMS is FDA-approved for depression and can help by stimulating mood-regulating brain areas.
Supporting Neuroplasticity and Brain Healing
An interruption of blood supply to the brain can cause damaged neural connections that need to be rebuilt to restore healthy functioning.
How TMS helps:
TMS encourages the brain to rewire itself by strengthening neural pathways, helping patients regain lost functions over time.
TMS Can Help Treat Dystonia
Current Limitations & Considerations
- Still Experimental: TMS is not yet an FDA-approved treatment for dystonia, but clinical trials are ongoing.
- Response Varies: Different types of dystonia (e.g., focal vs. generalized) may respond differently to TMS.
- Best Results with Repeated Sessions:
Effects may wear off over time, requiring ongoing treatment.
Dystonia is a type of neurological movement disorder that causes abnormal muscle contraction. Involuntary muscle contractions can lead to twisting or repetitive movements that are associated with poor posture and pain.
Modulating Abnormal Brain Activity
Dystonia is linked to dysfunctional motor circuits in the brain, particularly in the basal ganglia, primary motor cortex, and premotor areas.
How TMS helps:
Low-frequency TMS (inhibitory) can reduce excessive cortical excitability, which contributes to involuntary muscle contractions.
High-frequency TMS (excitatory) may stimulate underactive brain regions involved in motor control.
Reducing Muscle Spasms & Improving Motor Control
Involuntary muscle contractions can lead to spasms and other feelings of discomfort. This abnormal muscle activity can also interfere with motor control, creating barriers to completing simple and complex physical tasks.
How TMS helps:
TMS can be targeted at the primary motor cortex (M1) to help regulate muscle contractions and improve coordination.
Studies suggest that repetitive TMS (rTMS) over M1 can lead to improved movement and reduced muscle stiffness.
Enhancing Neuroplasticity & Motor Learning
Motor processing can be limited by abnormal neural activity.
How TMS helps:
TMS promotes neuroplasticity, helping the brain reorganize neural pathways to restore more normal movement patterns.
This effect may be especially helpful for task-specific dystonia (e.g., musician’s or writer’s cramp).
Potential for Long-Term Symptom Relief
Although there is no cure for dystonia, treatments can significantly alleviate symptoms.
How TMS helps:
Some studies suggest that repeated TMS sessions can lead to long-lasting improvements in dystonia symptoms, though effects vary by individual.
Complementing Other Treatments
Dystonia is complex, with heterogeneous etiologies and symptomology, often requiring a multidisciplinary care team.
How TMS helps:
TMS is often used alongside physical therapy, botulinum toxin (Botox) injections, and medication for a more comprehensive approach to dystonia treatment.
Conclusion
TMS harnesses advanced technology that has the potential to be life-changing for many different clinical populations. Ongoing research produces valuable insight into the therapeutic applications of this cutting-edge technology and how we can support a wider range of patients.

"Dr. Simonsen and his staff were great! They were patient and accommodating during my TMS journey. I always felt comfortable during my appointments. Highly recommend!"
Brittney M.
Evidence-Based Care You Can Trust
Services & Resources
Tailored Care, Built Around You
Featured Resources
Is TMS Right For Me?
Valuable questions to ask yourself while making your decision about what treatment pathway to pursue!
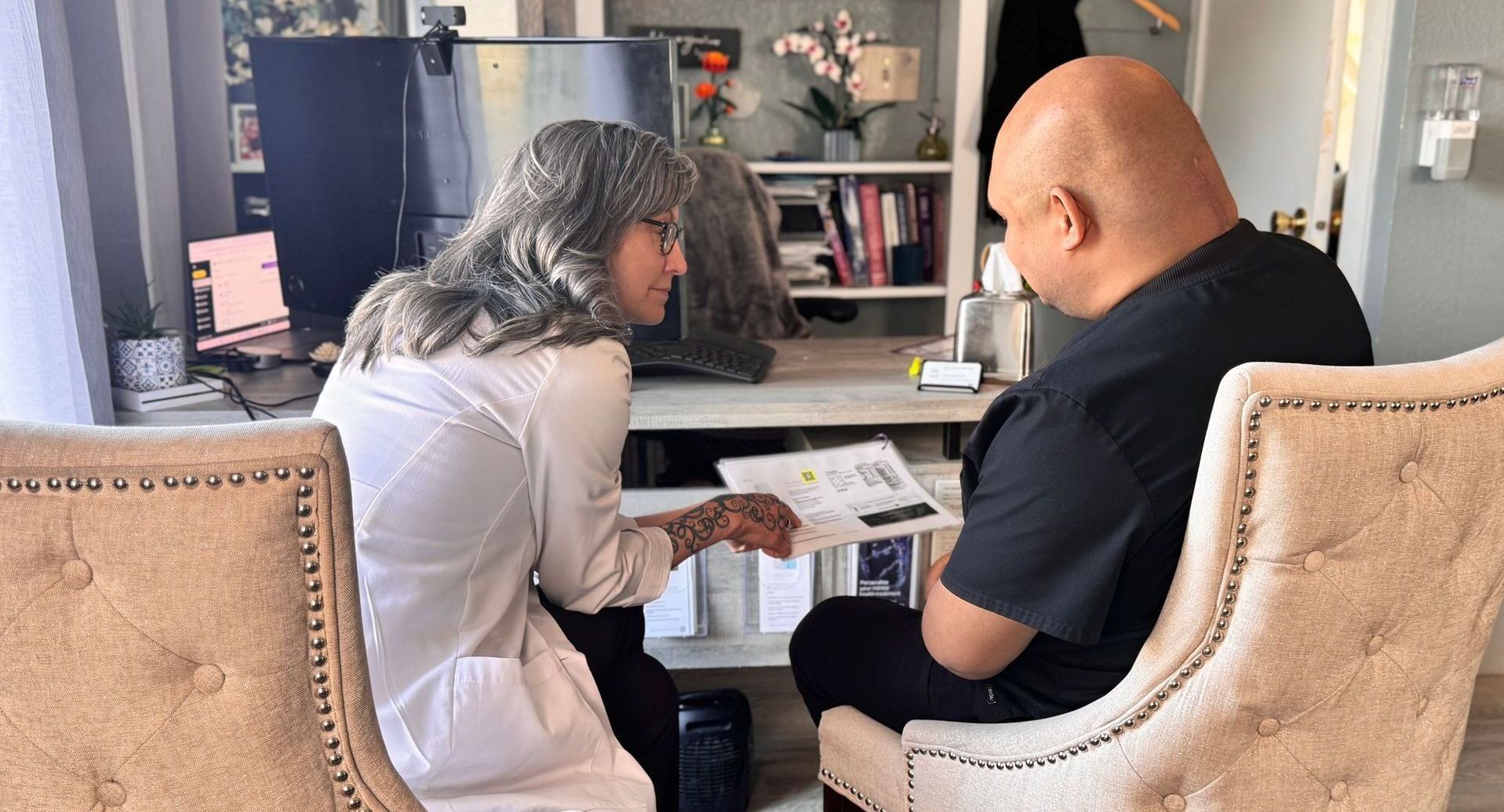

What to Expect?
The critical stages of our treatment options to ensure you enter your appointments with confidence.
Benefits & Side Effects
TMS is a brain stimulation technique that aims to manage mental health symptoms

83%
of patients experienced symptom improvement, with
62% achieving full remission
after completing TMS.
"From the first visit, Creative Wellness exceeded my expectations. Dr. Keays and her staff are genuine, the results are real, and the atmosphere is empowering. The care that I received from Creative Wellness has transformed my life enormously."
"I cannot say enough about Creative Solutions, Dr. Simonsen, his staff, and TMS. I was skeptical but decided to give it a try. They were very thorough in explaining the what's/why's/how's and extremely professional every step of the way. I feel better than I have in YEARS."
"TMS therapy was super helpful, I came to him with severe depression and taking meds that helped very minimally! I was impressed with how quickly I noticed changes with my mental health and my desire to actually want to get up and do things where as before I had zero desire for anything! "
Request Appointment
For more details or to schedule a consultation, give us a call at 253-900-1605 or fill out our online form.